Morning View
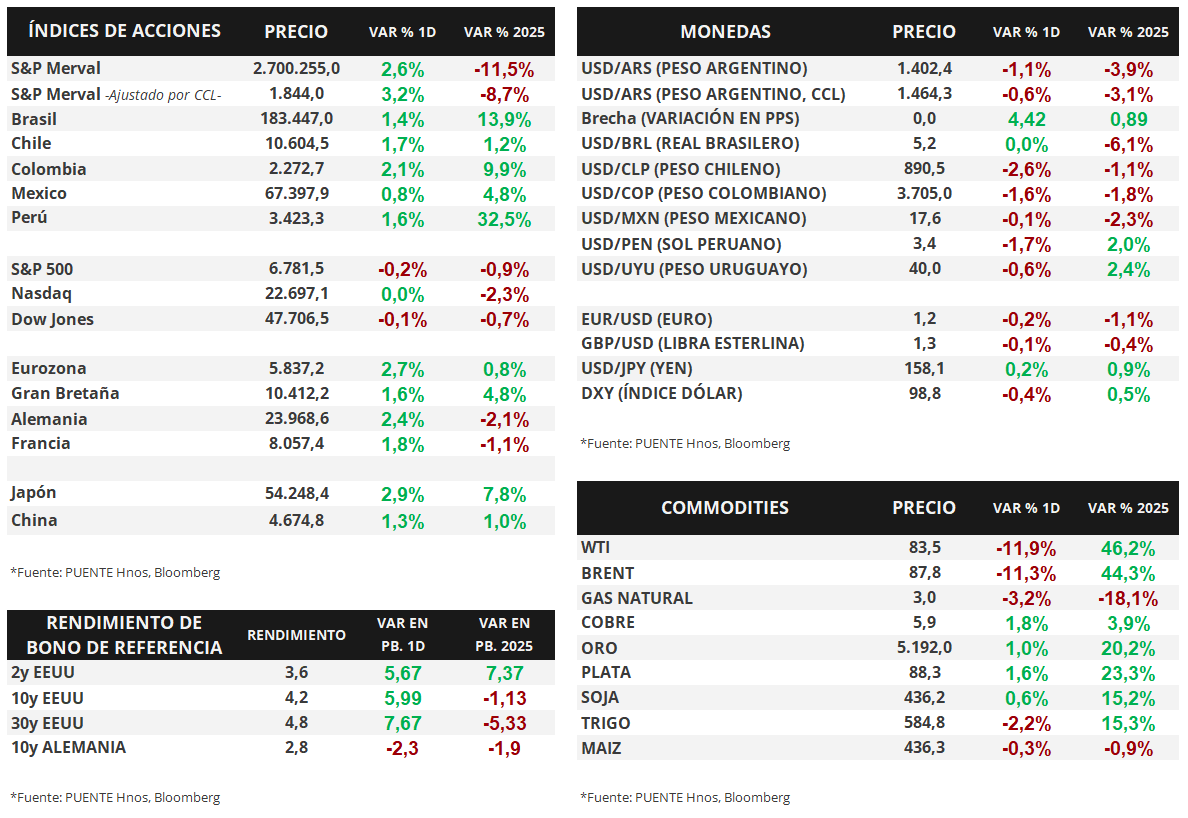
The main US stock indexes closed mixed on Wednesday
International
Yesterday, following the release of February inflation data, which was in line with projections, the main US stock indices remained virtually unchanged. The S&P 500 fell -0.1%, while the Nasdaq rose +0.1%. The Dow Jones, meanwhile, fell -0.6%. Thus, so far this year, the indices have accumulated variations of -1.0%, -2.3%, and -1.3%, respectively.
As for US Treasury bond yields, the curve widened again yesterday. The yield on the 1-year bond rose from 3.55% to 3.58%, while the 3-year bond widened its yield from 3.61% to 3.67%. Following the same trend, the 10-year yield rose from 4.16% to 4.23%.
Finally, commodities trended upward overall. Metals were the exception, with gold suffering a slight decline of -0.3%, closing at USD 5,177 per ounce, while soybeans advanced +1.1% and closed at USD 441.2 per ton. Oil was once again the star of the day, with WTI crude oil rising +5.5% and Brent crude oil rising +5.6%, closing at USD 88.1 and USD 92.7, respectively.
Source: PUENTE Hnos, Bloomberg
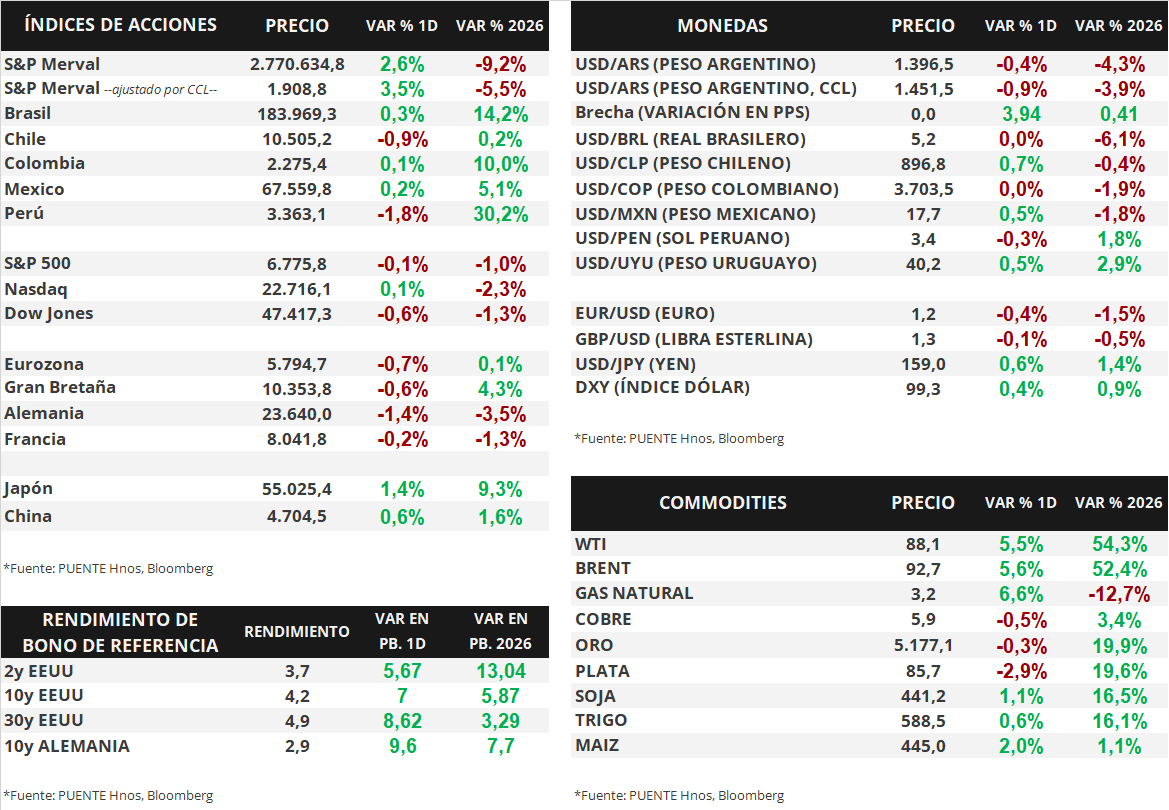
February inflation in the United States stands at +2.4% year-on-year
International
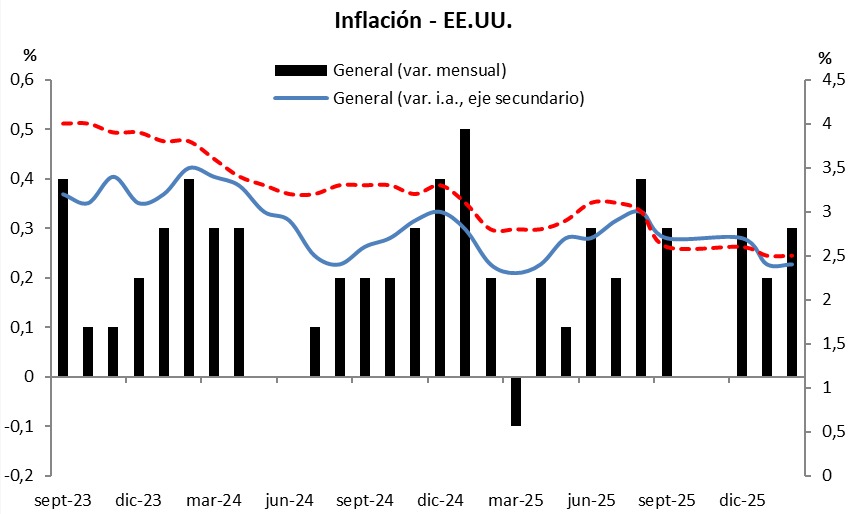
This morning, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) was published in the United States. The data, corresponding to February, stood at +0.3% monthly and +2.4% year-on-year, in line with analysts' consensus projections. On the other hand, the core measurement, which excludes food and energy, was +0.2% monthly and +2.5% year-on-year, also in line with analysts' expectations.
The main US stock indices closed with slight changes on Tuesday. The S&P 500 fell -0.2%, the Nasdaq remained unchanged, and the Dow Jones fell -0.1%. Thus, so far this year, the indices have accumulated variations of -0.9%, -2.3%, and -0.7%, respectively.
As for U.S. Treasury bond yields, the curve widened yesterday. The yield on the 1-year bond rose from 3.53% to 3.55%, while the 3-year bond widened its yield from 3.56% to 3.61%. Similarly, the 10-year yield rose from 4.10% to 4.16%.
Fuente: PUENTE Hnos, Bloomberg